The rate of diffusion. He established the relationship through experiments.
Can The Rate Of Effusion Or Diffusion Be Negative In Accordance With Graham S Law If So How Quora
Grahams law also applies to effusion the process in which gas molecules flow through a small hole in a container.
Graham's law of effusion. This is not to be confused with diffusion which declares that molecules will move from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration. But if time is used the equation changes Grahams Law deals with the effusion of gases. Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of.
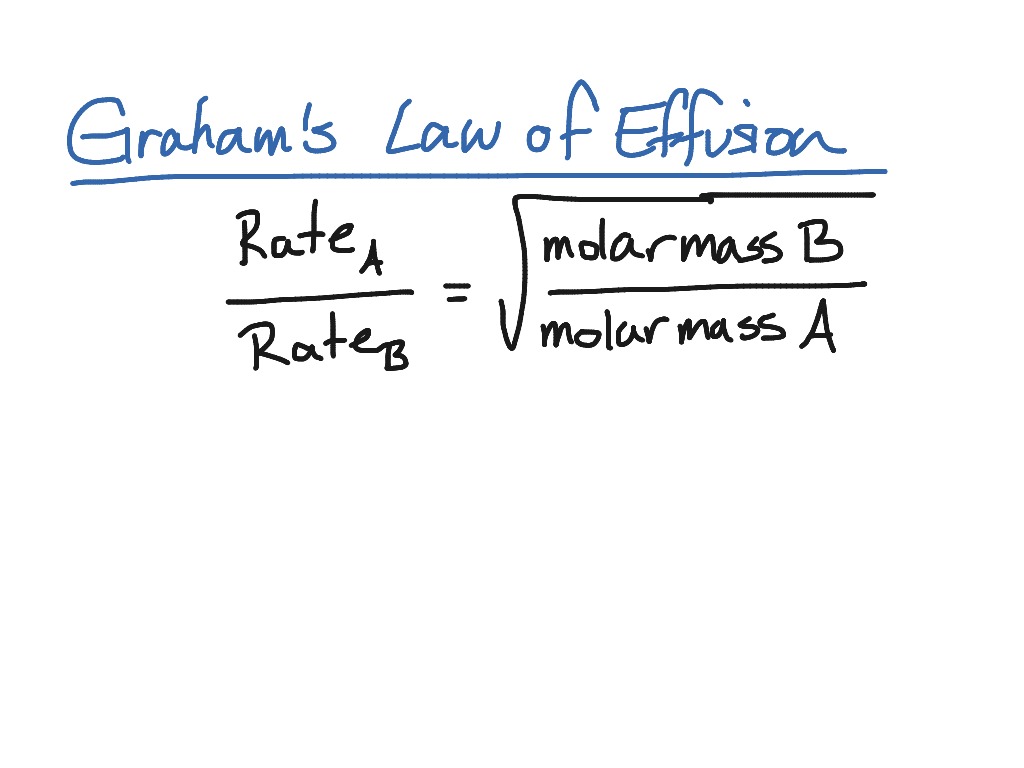
Grahams law states that the rate of effusion or diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight. This empirical law was stated by Scottish chemist Thomas Graham in 1848. Rate1 Rate2 M2 M1 12 Where.
Grahams law of diffusion or Grahams law of effusion is a law that expresses the relationship between the rate of diffusion or effusion to molar masses of particles. That means we are mostly looking at amounts that move per unit time not how fast the individual particles are moving. Rate1 is the rate of effusion of one gas expressed as volume or as moles per unit time.
Usually this formula is used when comparing the. Grahams Law is a relation which states that the rate of the effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density or molecular mass. This grahams law of effusion chemistry video tutorial contains the plenty of examples and practice problems for you to work.
He also gave the rate at which molecules would escape ie. When we are applying this law for the diffusion of a gas first we need to know what is diffusion. R M½ constant.
Different gases diffuse at different rates depending on their molar masses. Grahams Law which is popularly known as Grahams Law of Effusion was formulated Thomas Graham in the year 1848. Grahams Law of Effusion Grahams law states that the rates of effusion of two gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molar masses at the same temperature and pressure.
5 Use Grahams Law. Where g is the mass lost A is the area of the orifice D t is the time the effusion is allowed to proceed T is the temperature and M W is the molar mass of the compound in the vapor phase. It helps in the separation of isotopes of certain elements.
R 1 M½. Thus if the molecular weight of one gas is four times that of another it would diffuse through a porous plug or escape through a small pinhole in a vessel at half the rate of the other heavier gases diffuse more slowly. Thomas Graham experimented with the effusion process and discovered an important feature.
Grahams law of Effusion or diffusion states that when the temperature and pressure are constant than atoms with high molar mass effuse slower than atoms with low molar mass. Grahams law states that the rate of diffusion or of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight. Importance of Grahams law of diffusion - definition It helps in the separation of gases having different densities.
This became known as Grahams Law and it states that the effusion rate of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular mass. Grahams law states that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Grahams law of diffusion is a law in chemistry which indicates that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass.
Grahams Law says that at constant temperature and pressure rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of molecular mass of gas So for two gases with Molecular mass M 1 and M 2 their rate of diffusion will be related by. 2 1 x 1 x 4 6 Our heavier gas is four times heaver than the lighter gas remember that the lighter is effusing twice as fast as the heavier gas. You can compare the rates at which two gases diffuse using Grahams law.
Grahams Law states that the effusion rate of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles. Grahams Law deals with the effusion of gases. The principle of effusion depends upon a movement or diffusion of gases but it relates to the rate of travel of a gas through a predefined.
It contains the equation or fo. Effusion refers to the movement of gas particles through a small hole. The pressure is then given by p.
In Grahams Law we will look at the rate of effusion movement of gas through a small pinhole into a vacuum more often than we will look at a speed like a root mean square speed. A schematic of what a Knudsen cell might look like is given below. See this law in equation form below.
Gas molecules that are lighter will travel faster than the heavier gas molecules. In these equations r rate of diffusion or effusion and M molar mass.
 Graham S Law Of Effusion Molar Mass Mcat Science
Graham S Law Of Effusion Molar Mass Mcat Science
 Graham S Law Of Effusion And Diffusion Chemistry Steps
Graham S Law Of Effusion And Diffusion Chemistry Steps
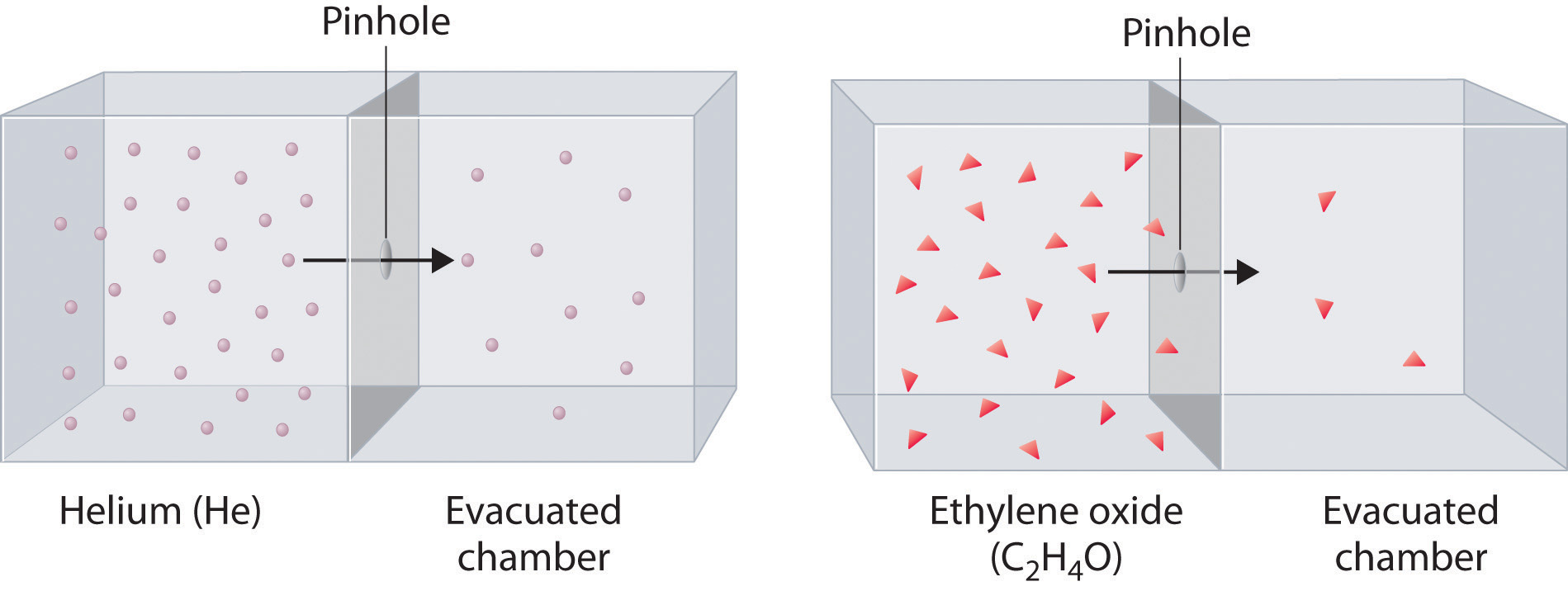 2 9 Graham S Laws Of Diffusion And Effusion Chemistry Libretexts
2 9 Graham S Laws Of Diffusion And Effusion Chemistry Libretexts
 Graham S Law Of Diffusion And Effusion Chemistrygod
Graham S Law Of Diffusion And Effusion Chemistrygod
 Graham S Law Of Diffusion Chemistry Hybrid
Graham S Law Of Diffusion Chemistry Hybrid
 Graham S Law Of Diffusion And Effusion Formula Definition Diagrams
Graham S Law Of Diffusion And Effusion Formula Definition Diagrams
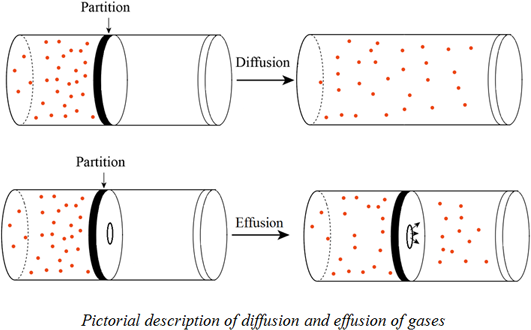 Definition Of Graham S Law Chegg Com
Definition Of Graham S Law Chegg Com
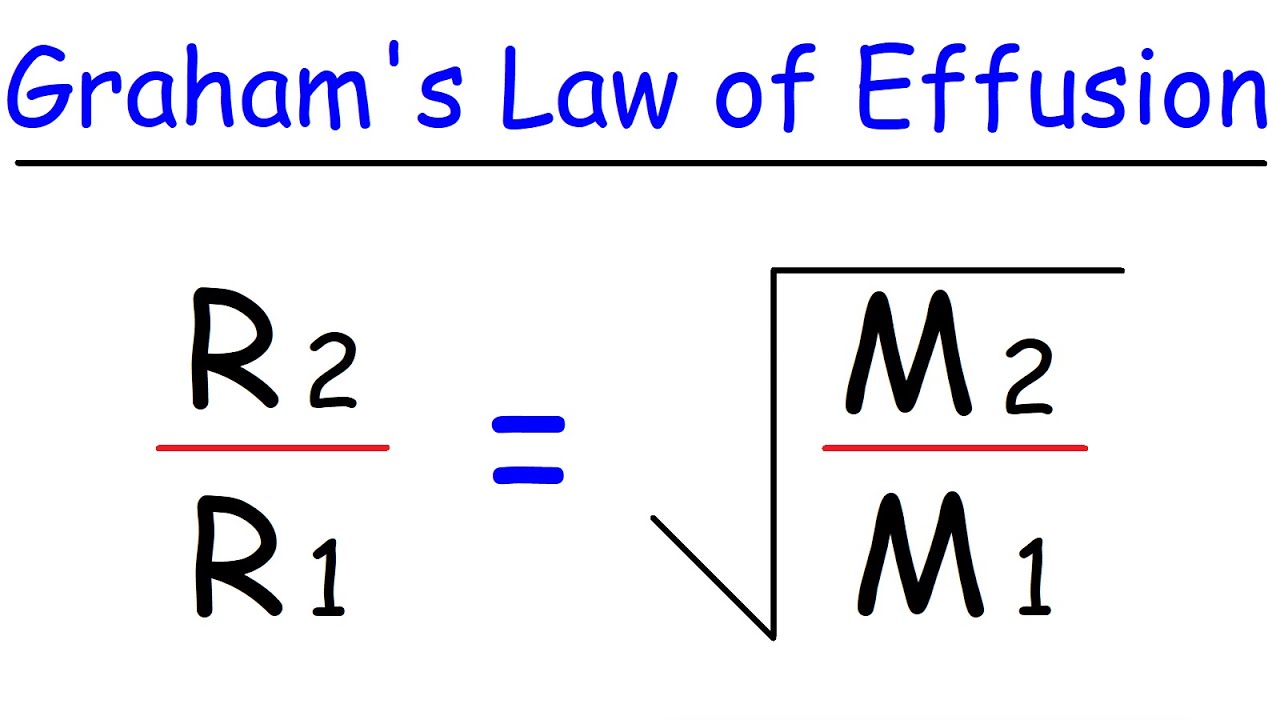 Graham S Law Of Effusion Youtube
Graham S Law Of Effusion Youtube
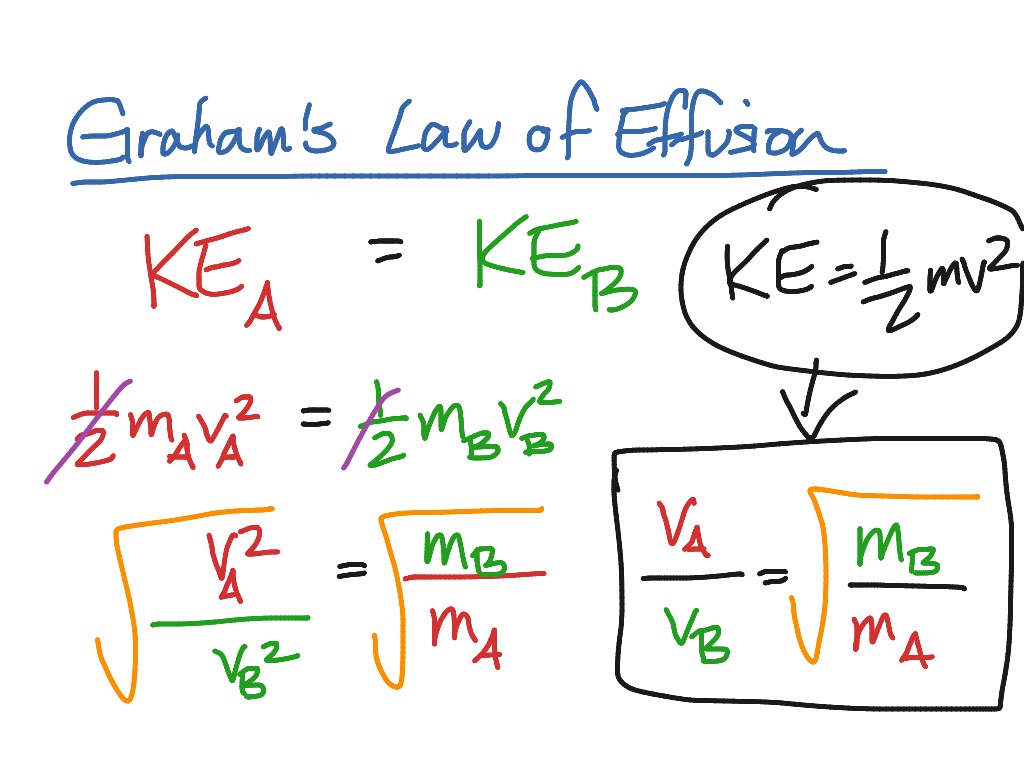 Derivation Of Graham S Law Of Effusion Chemistry Gas Laws Science Gases Showme
Derivation Of Graham S Law Of Effusion Chemistry Gas Laws Science Gases Showme
 Understanding Graham S Law Of Effusion Youtube
Understanding Graham S Law Of Effusion Youtube
 Derivation Of Graham S Law Of Effusion Chemistry Gas Laws Science Gases Showme
Derivation Of Graham S Law Of Effusion Chemistry Gas Laws Science Gases Showme
Graham S Law Calculator Calistry
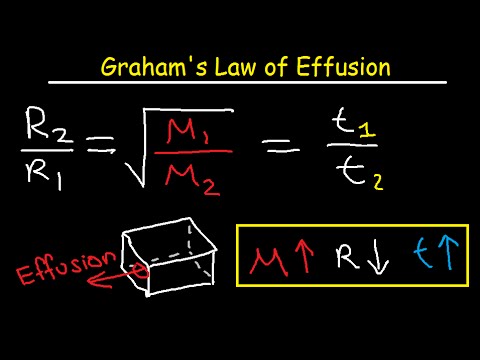 Graham S Law Of Effusion Practice Problems Examples And Formula Youtube
Graham S Law Of Effusion Practice Problems Examples And Formula Youtube
