So the pKa is equal to the negative log of 29 times 10 to the negative 16. If pH is more than pKa its mainly deprotonated.
A small Ka value means little of the acid dissociates so you have a weak acid.
Ph pka log base acid. PH pKalogbase acid p H p K a l o g b a s e a c i d D The relative molecular mass is not related to the pKa of the weak acid. This scale goes either way if pH is less than pKa then its mainly protonated acid. Calculate by pH pKa log BaseAcid.
In these systems the compound from which this solution is obtained is ceCO2 produced in cell respiration which is converted into ceHCO3- and ceH2CO3 inside the red blood cells. PH gives an idea about the amount of H ions present in the medium. In this case the pH will just be equal to the pKa.
PKa is the logarithm of K a value. PH is the reciprocal of the logarithm of H concentration. The negative log of the dissociation constant which is a measure of strength of an acid.
Ka - the acid dissociation constant of the weak acid. Then use the fact that the ratio of A to HA 110 01. This Site Might Help You.
PH 475 log 10 01 475 1 375. PH pKa log conjugate base weak acid pH pkalog A - HA pH is the sum of the pKa value and the log of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the weak acid. At half the equivalence point.
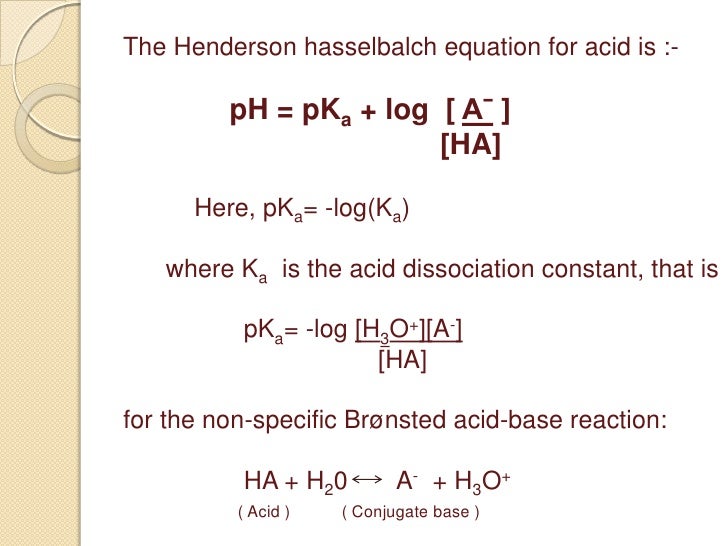
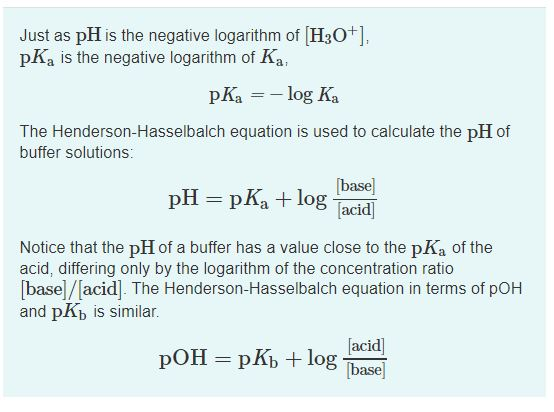
PH p K a log 10 Base Acid displaystyle ce pH ce pK_ ce alog _ 10left frac ce Base ce Acidright can be used to estimate the pH of a buffer. At the 1 pH unit above below the pK a the acid is 90 deprotonated protonated. In chemistry and biochemistry the HendersonHasselbalch equation.
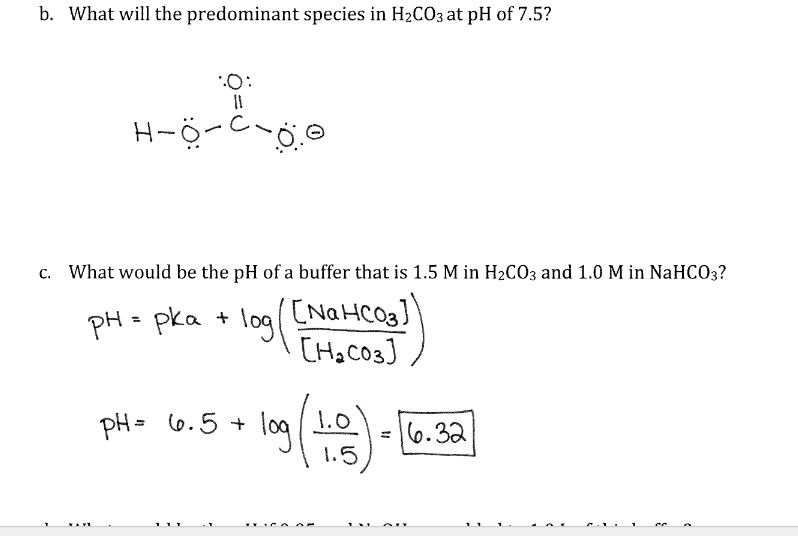
At the pK a the acid is 50 deprotonated. Equation used to estimate the pH of a weak acid or base solution. PH pKa Log HCO3-H2CO3 Where HCO3- and H2CO3 are conc of base and acid in buffer solution.
PKa logKa where. So the percentage ionization will be ionized1 110 pH pKa 100. The most common form of the Hendeson - Hasselbalch equation allows you to calculate the pH of a buffer solution that contains a weak acid and its conjugate base.
PH pKa Log baseacid. Hyperventilating Increase blood PH because CO2 leave the plasma rapidly during hyperventilation. If we wanted to find the pKa for methanol all we have to do is take the Ka and take the negative log of it.
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation answer. Lets talk about pKas. A large Ka value also means the formation of products in the reaction is favored.
But again theyre all considered to be weak acids relative to the stronger ones. At 3 pH unit above below the pK a the acid is 999 deprotonated protonated. Consider the Titration of 800 mL of 0100 M BaOH2 by 0400M HCL.
If the pH of a solution the pKa then the acid is in equilibrium it is half dissociated. Given the pK a of a weak acid HA for instance many students struggle to calculate the pH of a solution of the conjugate base A at concentration C pHA CThe traditional method involves calculating the base dissociation constant K b and the artificial quantity pOH. At 2 pH unit above below the pK a the acid is 99 deprotonated protonated.
When fully protonated charge on acetic acid is 0. Also you may be asked to rearrange this equation to find either S this is the salt or A the acid. BBH 10 pH pKa Here the portion of unionized form is 10 pH pKa whereas ionized form is 1.
The pKa is defined as the negative log of the Ka. PH pKa logA-HA pH pKalogconjugate baseundissociated acid The actual meaning of pKa. PHpKa log BBH Now the ratio of unionized to ionized forms of the base can be written as.
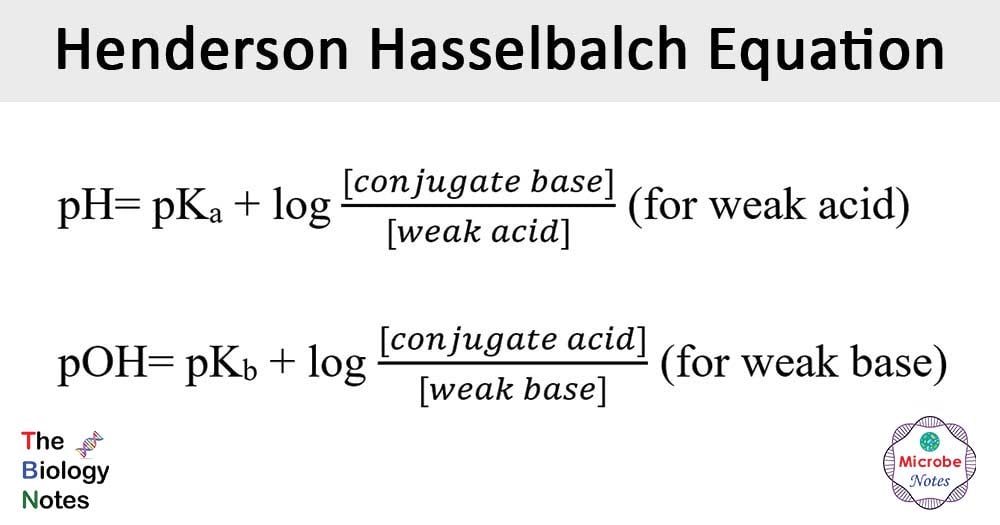
PH pKa log conjugate base weak acid Here pKa is equal to. Given the overall reaction CO2 g H2 O l H2 CO3 aq HCO3 - aq H aq what effect would each of the following have on blood pH. PH pKa log SA Theres no rhyme or reason to this equation simply just memorize.
PKa pH - logA-HA pH pKa logSALTACID Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation for Acid-Buffer Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation For Base Buffer BOH B 1 OH-1 Kb B OH-BOH take -log for each side of equation-log Kb -logOH- - logB BOH p -log pKb pOH - logB BOH pOH pKb logSALTBASE Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation for Base Buffer. Calculate pH of the resulting solution after the following volumes of HCL have been added. Undergraduate biochemistry students frequently find the quantitative treatment of weak acids and bases troublesome.
Calculate the ionization of a 0050 M solution of a base with the Kb 42x10-2. At half the equivalence point pH pKa -log Ka. PKa value gives an idea about to which side the equilibrium is favored the degree of acid dissociation.
At higher pH values more than half will be ionized. This means that at pH lower than acetic acids pKa less than half will be dissociated or ionized. Now writing Hendersen-Hasselbalch equation for the conjugate acid.
Both pH and pKa are related by Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions. Buffer solutions are used by biological mammalian systems to maintain the mathrmpH of blood plasma within a narrow range.
 How To Calculate Pka From Ph Quora
How To Calculate Pka From Ph Quora
 Bt Gs 1 9 Describe Factors Influencing The Distribution Of Drugs For Example Ph Pka Primary Lo Of The Day
Bt Gs 1 9 Describe Factors Influencing The Distribution Of Drugs For Example Ph Pka Primary Lo Of The Day
 Understanding Chemistry How Ph And Pka Are Related
Understanding Chemistry How Ph And Pka Are Related
 Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes
 Acid Base Theory Ph Calculations Ppt Download
Acid Base Theory Ph Calculations Ppt Download
 Ppt Acid Base Titrations Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3207796
Ppt Acid Base Titrations Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3207796
 Solved I Understand The Ph Pka Log Base Acid Equatio Chegg Com
Solved I Understand The Ph Pka Log Base Acid Equatio Chegg Com
 Solved Just As Ph Is The Negative Logarithm Of H30 Pk Chegg Com
Solved Just As Ph Is The Negative Logarithm Of H30 Pk Chegg Com
 Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Acid Base Buffer Chemistry Introduction Ph Pka Log A Ha Youtube
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Acid Base Buffer Chemistry Introduction Ph Pka Log A Ha Youtube
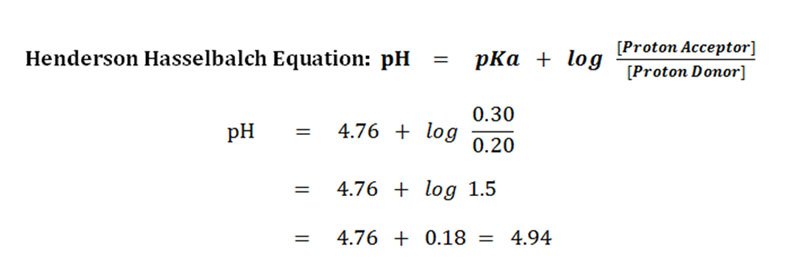 Solved Problems Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Ph Pka Easy Biology Class
Solved Problems Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Ph Pka Easy Biology Class
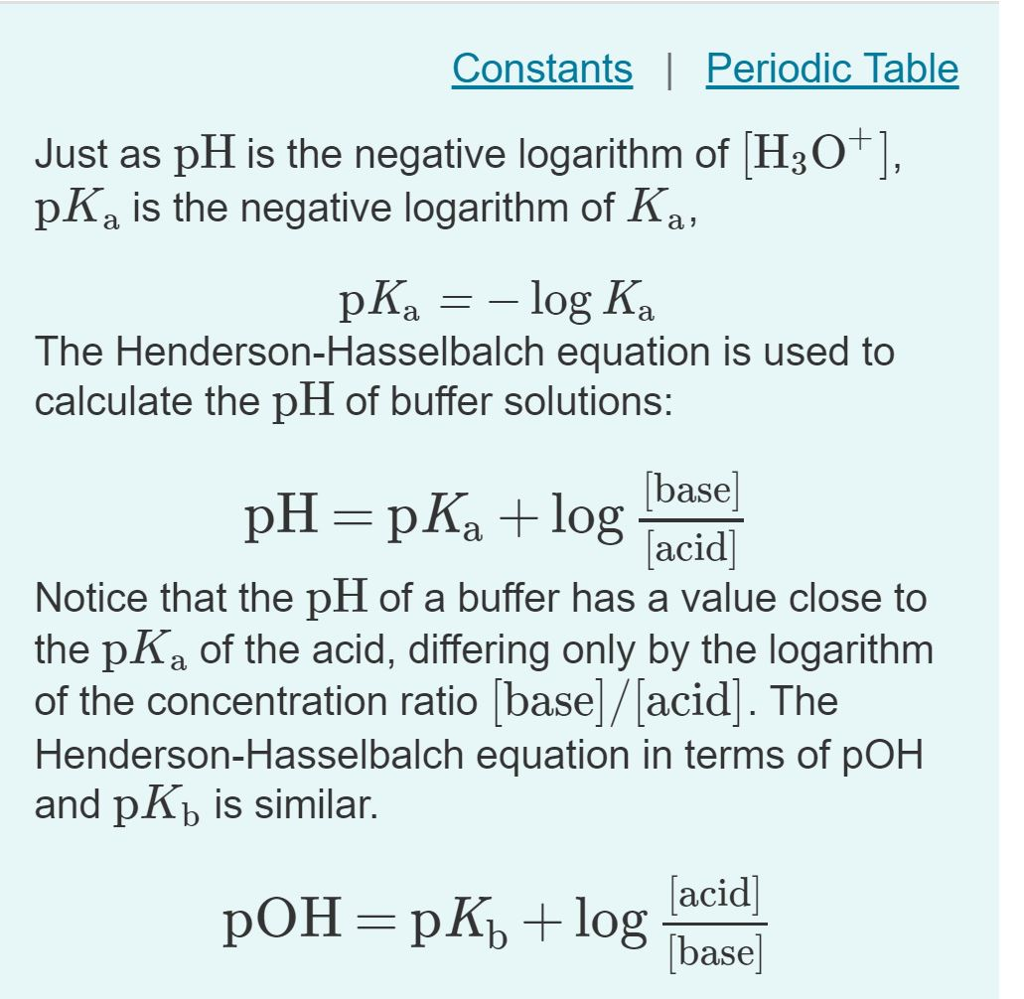 Solved Constants Periodic Table Just As Ph Is The Negati Chegg Com
Solved Constants Periodic Table Just As Ph Is The Negati Chegg Com
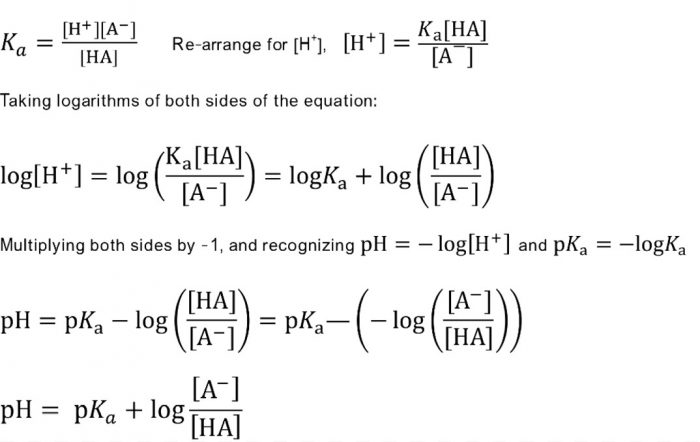 Calculation Of Ph Of A Buffer Mixture Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
Calculation Of Ph Of A Buffer Mixture Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium